Syria’s Road to Stability: Kurdish Democratic Federalism as a Pathway Forward
An examination of how the Kurdish vision for a decentralised Syria offers a viable framework for sustainable peace, minority protection, and regional stability.

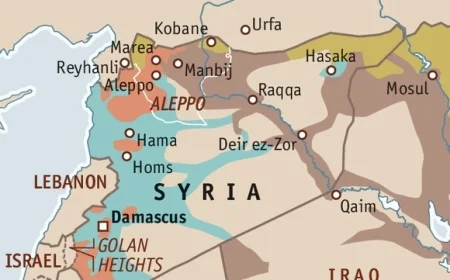
The ongoing Syrian conflict has reshaped political realities across the Middle East, with Kurdish forces emerging as crucial stakeholders in determining Syria’s future governance structure. Recent diplomatic initiatives have highlighted the Kurdish position: a democratic, decentralised Syria that respects ethnic diversity and ensures regional autonomy. This stance, articulated through the Syrian Democratic Council (SDC), represents more than self-interest—it offers a potential blueprint for addressing the fundamental governance failures that precipitated Syria’s descent into civil war.
Historical Context
Syria’s centralised governance model, dominated by a singular ethno-political group, has historically marginalised minority communities. The Kurdish population, comprising approximately 10% of Syria’s pre-war population, endured systematic discrimination under successive regimes, including denial of citizenship, cultural expression, and political representation. Similar exclusionary policies affected other minority groups, including Assyrians, Yazidis, and various Christian denominations.
When civil war erupted in 2011, this centralised power structure proved catastrophically unsuitable for managing Syria’s complex ethnic and religious mosaic. The subsequent power vacuum allowed extremist organisations to exploit sectarian grievances, most notably manifested in the Islamic State’s campaign of terror against minority populations.
The Kurdish Democratic Project
Against this backdrop, Kurdish authorities in northern Syria have implemented a governance model predicated on democratic confederation, gender equality, and multi-ethnic representation. This system, operational across much of northern Syria, has demonstrated remarkable resilience despite extraordinary challenges:
• Successful resistance against Islamic State forces when conventional militaries faltered
• Establishment of representative councils that provide proportional representation to all ethnic communities
• Implementation of co-presidency systems ensuring gender parity in leadership positions
• Protection of religious freedoms and minority rights in territories under Kurdish administration
The Kurdish position, advocating for a federal Syria with significant regional autonomy, stems from this practical governance experience rather than theoretical idealism. Their model addresses the fundamental challenge of providing responsive governance in a multi-ethnic society while maintaining territorial integrity.
International Dimensions
The Kurdish democratic project intersects with numerous regional and international interests. Turkey views autonomous Kurdish regions with suspicion, fearing spillover effects on its own Kurdish population. Meanwhile, the United States has relied heavily on Kurdish forces as ground partners against Islamic State militants, creating complex alliance dynamics.
Russia, backing the Assad regime, has shown pragmatic flexibility regarding potential decentralisation, recognising that Syria’s pre-war centralised model proved unsustainable. The European Union generally supports greater minority protections but remains wary of territorial fragmentation.
Within this intricate diplomatic landscape, Kurdish representatives have demonstrated remarkable strategic patience, maintaining dialogue with all major powers while adhering to democratic principles. Their consistent emphasis on Syria’s territorial integrity, coupled with insistence on decentralised governance, offers a middle path between complete fragmentation and destructive recentralisation.
Challenges to Federalism
Several significant obstacles confront the Kurdish vision:
1. The Assad regime remains committed to restoring centralised control over all Syrian territory.
2. Turkish opposition to any form of Kurdish autonomy creates persistent security threats.
3. Regional powers fear that federal models might inspire similar movements within their own borders.
4. International stakeholders frequently prioritise short-term security concerns over long-term governance solutions.
Additionally, internal Syrian opposition groups often view federalism through sectarian lenses rather than as a pragmatic governance solution. This mischaracterisation undermines potential cross-ethnic alliances that could strengthen the case for decentralisation.
Strategic Recommendations
For the Kurdish democratic project to succeed as a template for broader Syrian governance, several strategic approaches merit consideration:
Diplomatic Engagement
Kurdish authorities should continue emphasising that federalism serves all Syrians, not exclusively Kurdish interests. Specifically:
• Frame decentralisation as necessary protection for all minority communities, including Arabs, Turkmen, and Christian groups currently under authoritarian pressure.
• Highlight successful multi-ethnic governance in Kurdish-administered regions.
• Counter narratives that equate federalism with secession through consistent support for Syrian territorial integrity.
Institutional Development
The credibility of federalism depends on demonstrable governance success:
• Continue strengthening transparent, accountable institutions in Kurdish-administered areas.
• Document and publicise successful cross-community conflict resolution mechanisms.
• Develop educational curricula that preserve cultural distinctiveness while fostering shared civic identity.
International Advocacy
Kurdish representatives should develop targeted messaging for different international audiences:
• For Western powers: emphasise federalism as a bulwark against extremism and mass migration.
• For regional stakeholders: demonstrate how decentralisation can enhance stability without threatening borders.
• For multilateral institutions: align federal proposals with international norms on minority rights and self-determination.
Humanitarian Leadership
Kurdish authorities should continue demonstrating humanitarian commitment:
• Maintain exemplary treatment of displaced persons from all ethnic backgrounds.
• Facilitate international aid delivery to all communities in need.
• Document human rights conditions across Syria to strengthen accountability mechanisms.
Conclusion
The Kurdish vision for a decentralised, democratic Syria represents not merely an expression of Kurdish aspirations but a pragmatic response to Syria’s fundamental governance challenges. Their experiences in northern Syria demonstrate that inclusive, representative structures can function effectively even amidst conflict.
For Syria to emerge from its catastrophic civil war with sustainable peace, governance structures must address the exclusionary policies that fuelled the conflict initially. The Kurdish federalist proposal offers a framework for achieving this balance—preserving Syria’s territorial integrity while ensuring that all communities enjoy meaningful self-governance and cultural expression.
International stakeholders genuinely committed to Syria’s stability should recognise that sustainable peace requires more than military solutions; it demands governance structures that reflect Syria’s diverse reality. The Kurdish democratic project, tested under the harshest conditions imaginable, provides a viable path forward if given proper international support and recognition.
This approach would not only serve Syria’s diverse population but could potentially offer a governance template for other divided societies throughout the Middle East—a region where centralised authority has frequently failed to accommodate diversity. In this context, Kurdish democratic federalism represents not a challenge to state sovereignty but rather its evolution toward more sustainable forms.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0